Wind tunnel (Topic Discussion)
- Nelly
- July 21, 2024
- Board Games
A wind tunnel is a tool used in aerodynamics research to test the effects of airflow on objects such as aircraft, cars, buildings, and bridges. It simulates the movement of air around these objects in a controlled environment, helping engineers and designers understand and improve the performance of their creations.
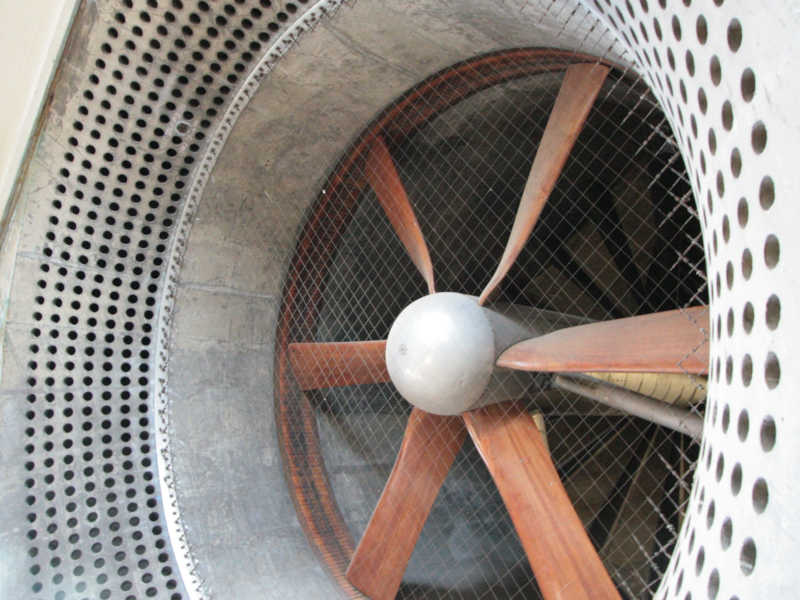
Wind tunnels come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from small tabletop models to large industrial facilities. The primary components of a wind tunnel include a test section where the object being studied is placed, a fan or compressor to generate airflow, and a series of sensors to measure parameters such as air velocity, pressure, and temperature.
One of the key advantages of wind tunnels is their ability to provide precise and repeatable test conditions. By controlling factors such as airspeed, temperature, and pressure, researchers can isolate and study specific aspects of aerodynamic performance. This allows them to make informed design decisions and optimize the efficiency and safety of their products.
Wind tunnels are used in various industries, including aviation, automotive, and civil engineering. In the aerospace sector, they are instrumental in the design and testing of aircraft, from commercial airliners to fighter jets. By subjecting scale models or full-size prototypes to controlled airflow, engineers can identify areas of improvement and enhance the overall aerodynamic performance of the aircraft.
In the automotive industry, wind tunnels are used to test the drag and lift characteristics of vehicles, enabling designers to optimize fuel efficiency and stability. By fine-tuning the shape of a car’s body, engineers can reduce air resistance and improve handling at high speeds.
In civil engineering, wind tunnels are utilized to study the effects of wind on structures such as bridges and skyscrapers. By understanding how airflow interacts with these buildings, designers can ensure they are resistant to wind-induced vibrations and capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions.
Despite their usefulness, wind tunnels have some limitations. For instance, they can be expensive to build and operate, making them inaccessible to smaller companies or research institutions. Additionally, the airflow in a wind tunnel may not always perfectly mimic real-world conditions, leading to discrepancies between test results and actual performance.
In conclusion, wind tunnels play a crucial role in aerodynamics research and development. They offer a controlled environment for studying the effects of airflow on various objects, helping engineers and designers make informed decisions and improve the performance of their creations. While they have some limitations, their ability to provide precise and repeatable test conditions makes them an essential tool in the design and optimization of aircraft, vehicles, and structures.




